Describe How Bacteria Develop Antibiotic Resistance
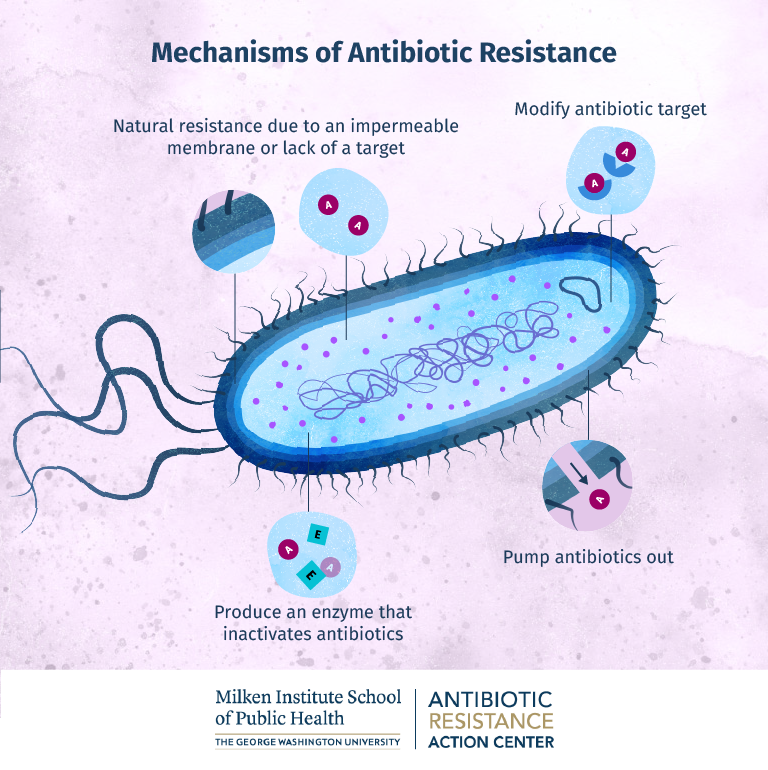
Antibiotics stop or interfere with a number of everyday cellular processes that bacteria rely on for growth and survival such as. The three fundamental mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance are 1 enzymatic degradation of antibacterial drugs 2 alteration of bacterial proteins that are antimicrobial targets and 3 changes in membrane permeability to antibiotics.
Print Materials And Fact Sheets Antibiotic Resistance Cdc
Bacteria can also acquire resistance.
. Crippling production of the bacterial cell wall that protects the cell from the external environment interfering with protein synthesis by binding to the machinery that builds proteins amino acid by amino acid. A random mutation occurs in the DNA of individual bacterial cells. That means the germs are not killed and continue to grow.
Bacteria that are resistant to many antibiotics are known as multi-resistant organisms MRO. Ways that bacteria acquire resistance. Antibiotic resistance happens when bacteria survive and continue causing infection despite treatment with an antibiotic the bacteria are no longer sensitive to that antibiotic.
The main one is through selective pressure. Acquisition of foreign DNA material through HGT is one of the most important drivers of bacterial evolution and it is frequently responsible for the development of antimicrobial resistance. Infections take longer to heal.
When antibiotic resistance happens fewer antibiotics are effective against a particular bacterium. Pump the antibiotic out from the bacterial cell. Because bacteria multiply A LOT there is a higher chance a mutation like this will occur.
They are able to survive and even multiply in the presence of an antibiotic. The main steps in the development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria are. Antibiotic resistant bacteria are bacteria that are not controlled or killed by antibiotics.
Mutation Through the process of cell replication some bacteria develop mutations that makes them resistant to antibiotics. Lack of antibiotics to treat infections caused by multi-drug resistant bacteria. Antibiotics and antifungals kill some germs that cause infections but they also kill helpful germs that protect our body from infection.
Fungi parasites and viruses can also develop drug resistance. Also if a person 18178 results page 15. Antibiotic resistance is accelerated when the presence of antibiotics pressure bacteria and fungi to adapt.
Every time a multiplication event happens there is a chance a mutation can occur. Antibiotic resistance is a type of antimicrobial resistance. 1 Cell entry - many antibiotics need to enter bacteria to kill them.
In the presence of drugs only drug-resistant bacteria survive. This happens when a type of bacteria changes in a way that protects it from the antibiotic. Bacteria with the resistant mutation have a better chance of survival against antibiotics.
Ad Over 27000 video lessons and other resources youre guaranteed to find what you need. The drug resistant bacteria multiply and thrive. How bacteria develop antibiotic resistance Jan 18 2021 Scientific research It is known that some bacteria and the infections they cause are much more difficult to fight than in the past even with high doses of antibiotics.
Sometimes when a bacterium is multiplying a random mistake in the bacteriums DNA will create a gene that gives it resistance to antibiotics. Because the antibiotic no longer works against the resistant bacteria. Antibiotic resistance happens when germs like bacteria and fungi develop the ability to defeat the drugs designed to kill them.
Other antibiotics often help but it is important to. The mutation protects the bacterial cell from the. Describe how bacteria develop antibiotic resistance.
Apparently most pathogenic microorganisms have the capability of developing resistance to at least some antimicrobial agents. Either through a new genetic change that helps the bacterium survive or by getting DNA from a bacterium that is already resistant. There are several ways for bacteria to become antibiotic-resistant.
Lack of a comprehensive uniform and coordinated response among all countries. These so-called efflux pumps are very common in bacteria and can transport a variety of compounds such as signal molecules and nutrients. Bacteria multiply by the billions.
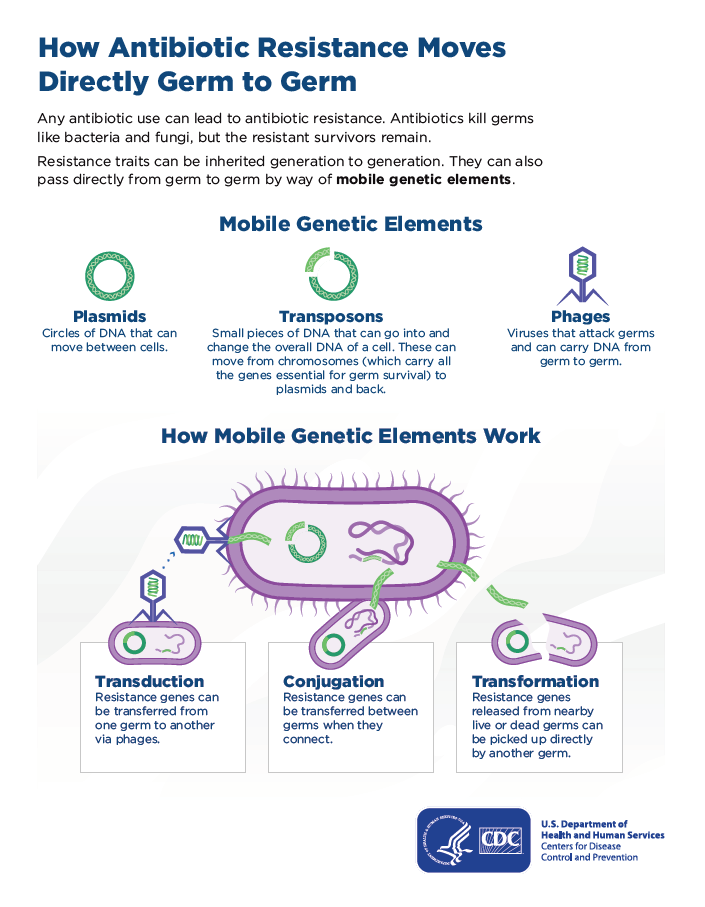
Infections can get worse and lead to more serious problems. The main mechanisms of resistance are. Bacteria that have drug resistant DNA may transfer a copy of these genes to other bacteria.
Your body doesnt develop antibiotic resistance bacteria do. Selective pressure happens when not all the bacteria are susceptible to the antibiotic used to treat the infection and the surviving bacteria can continue to multiply. Bacteria can produce pumps that sit in their membrane or cell wall.
More than 28 million antibiotic-resistant infections occur in the US. Limiting uptake of a drug modification of a drug target inactivation of. Bacteria develop antibiotic resistance when it changes in a manner in which reduces or eliminates the effectiveness of drugs chemicals or other agents designed to cure or prevent infections.
Antibiotic resistance can be either plasmid mediated or maintained on the bacterial chromosome. How do bacteria become resistant to antibiotics. Most antimicrobial agents used in clinical practice are or derive from products naturally found in the environment mostly soil.
Bacteria can acquire resistance in two ways. Most infection-causing bacteria can become resistant to at least some antibiotics. This is because some microorganisms are capable of developing specific resistance to antibiotics.
Non-resistant bacteria recieve the new DNA and become resistant to drugs. Weak or absent antibiotic resistance surveillance programs to track the number and type of antibiotic-resistant infections in a given area city country or global region. There are a number of ways bacteria can resist antibiotics.
Stop the antibiotic from reaching its target. Antibiotic resistance mechanisms 1.

How Bacteria Build Resistance At The Cellular Level Online Public Health

Antibiotic Resistance Health Navigator Nz


No comments for "Describe How Bacteria Develop Antibiotic Resistance"
Post a Comment